LECCIÓN 2 / Intermediate

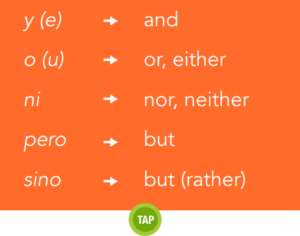
CONJUNCTIONS
probablemente cinco o seis.
I don’t know how many are coming . . .
probably five or six.
Sudamérica.
Neither Costa Rica nor Panama are in
South America.
mi novia no puede.
I’m going to the Chayanne concert, but my girlfriend can’t.
vasos, platos y tenedores.
I don’t have books in my backpack, but rather glasses, plates and forks.
Let’s look at some special cases that arise with some of these conjunctions:
★ When the conjunction “y” precedes a word that
begins with the letter “i” or the letters “hi,” the “y” normally becomes “e.” This change avoids having the “y” sound being swallowed up by the identical vowel sound that follows






BUT: Kentucky e Indiana
BUT: Ramón e Inés
BUT: jirafa e hipopótamo
★ Likewise, when the conjunction “o” precedes a word that begins with the letter “o” or the letters “ho,” the “o” becomes “u.” This change makes certain that the word “o” doesn’t become lost in the word that follows.






BUT: Harriet u Ozzie
BUT: piano u órgano
BUT: apartamento u hotel
★ The conjunction “pero” is replaced by the word “sino” in a negative sentence when there is a direct contradiction presented.






Pitbull is not tall, but rather short.
Today Sergio García didn’t play well, but poorly.
muñecas, sino de estampillas.
My sister doesn’t have a doll collection, but
rather a stamp collection.
I don’t want to go sailing this afternoon, but
rather swim.
Note: It’s useful to remember the translation “but rather” for “sino.” We may choose not to say “but rather” in English, but if we could, it means we need the Spanish word “sino.”
★ If the initial part of the statement is affirmative, or if there is no contradiction presented, use “pero.”






después.
We are going to the movies, but we can’t go to supper afterwards.
Sergio didn’t play well, but he’s happy.