LECCIÓN 1 / Beginner

VERBS IN THE PRESENT TENSE

Verbs are the words in a sentence that narrate the action; they tell you what is going on. Unlike in English, the letters at the end of a verb in Spanish let you know who the subject is. Once you learn these endings, you will be ready to speak complete Spanish sentences!
The infinitive of a verb is its simplest form, the starting place before it is conjugated or changed to correspond to a specific person.
All Spanish infinitives end in the letters AR, –ER, or –IR.
The present tense describes actions that are happening now, reports current conditions or traits, describes customary events, and also announces what may be happening in the immediate future.
Here are the full conjugations of three common verbs in the present tense:

Did you notice that -AR, -ER, and -IR verbs share some common endings but have different ones as well? Study the endings of the verbs carefully. They provide a clue to help you figure out who the subject is.
Cristina habla mucho.
Cristina speaks a lot.
Como chocolate en febrero.
I eat chocolate in February.
Vivimos en Chihuahua, México.
We live in Chihuahua, Mexico.
¿Come Miguel Vásquez mucha pizza?
Does Miguel Vásquez eat a lot of pizza?
¿Viven los tigres en África?
Do tigers live in Africa?
You may have noticed that the subject is sometimes mentioned (Cristina habla . . .) and at other times not (Como chocolate . . .). Because the ending of the verb helps to identify the subject, the subject is normally only mentioned for clarification or emphasis. In a statement in which the subject is mentioned, it is usually placed before the verb; in a question, however, it will follow the verb.
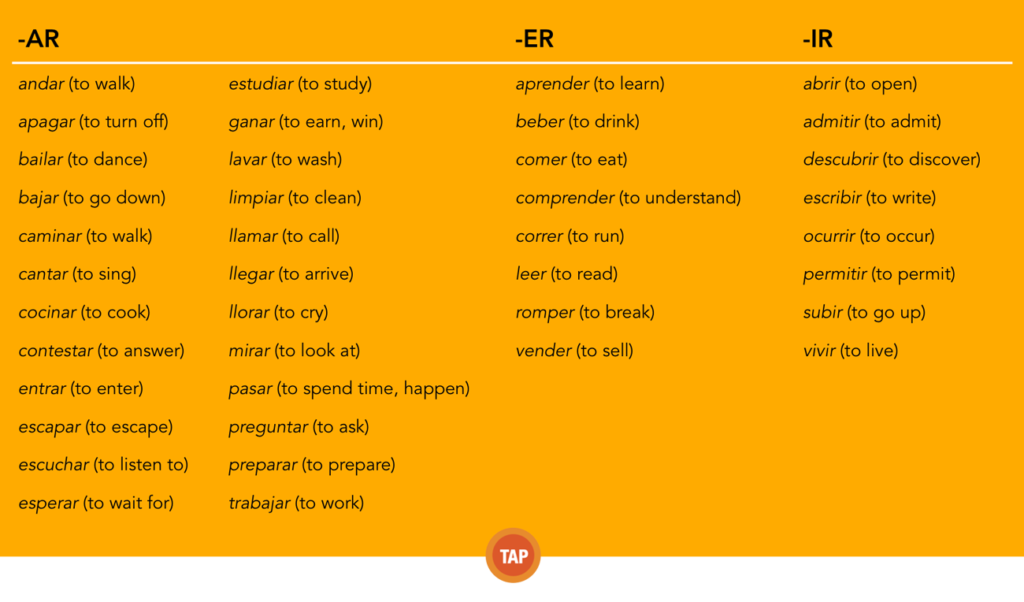
The following list contains some of the most frequently used verbs in the Spanish language. All of these verbs follow the conjugation patterns presented on the previous page. Although you do not need to know the meanings of all these words just yet, you will be noticing them throughout this book. In time, they will all become old friends.
Here is a list of some “high frequency” verbs:

EXAMPLES
Mi papá prepara tacos en el restaurante.
My dad prepares tacos in the restaurant.
¿Venden los artistas mucho arte?
Do the artists sell a lot of art?
¿Escribe el profesor mucho en julio?
Does the teacher write a lot in July?
Bailamos la salsa con la música de
Marc Anthony.
We dance the salsa with the music of Marc Anthony.